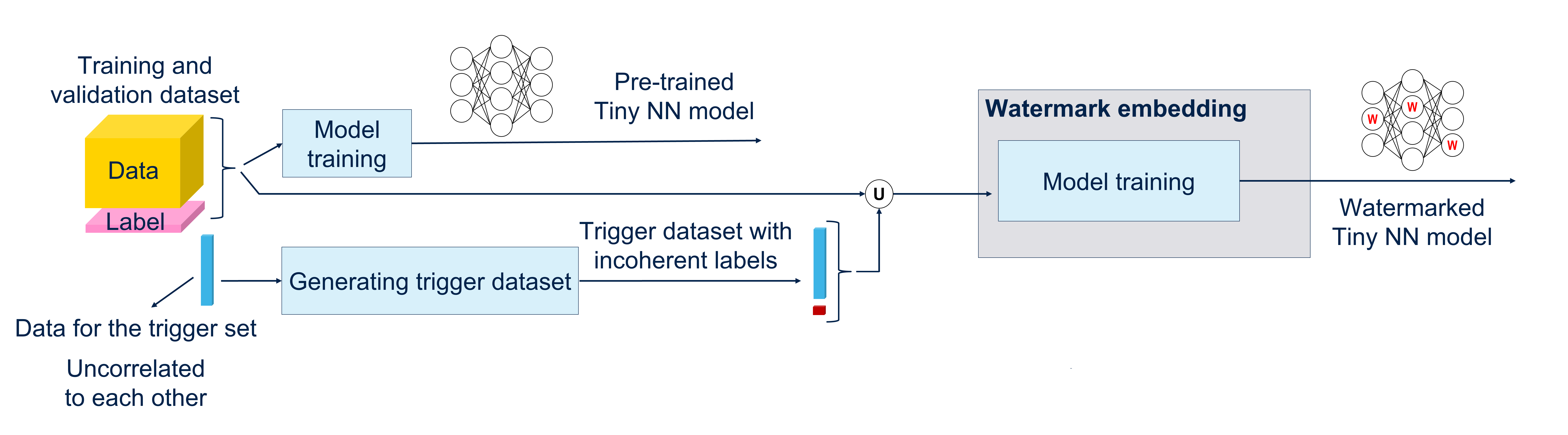
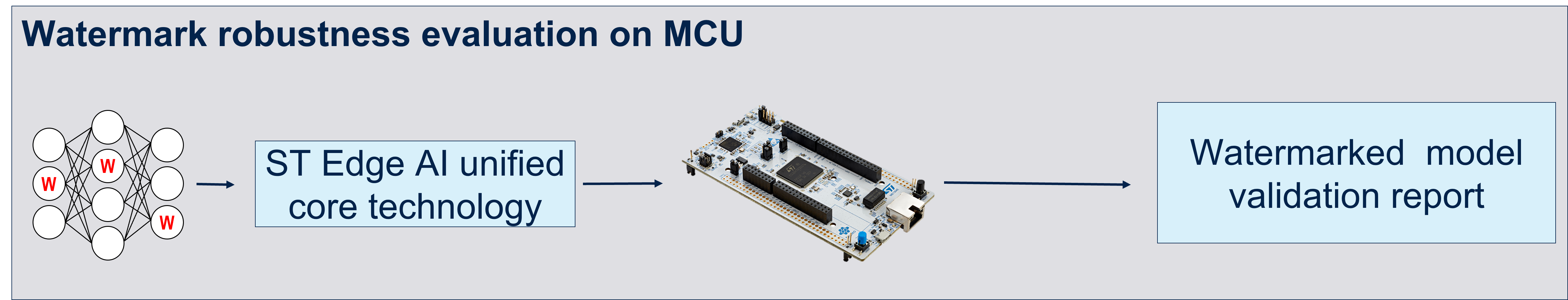
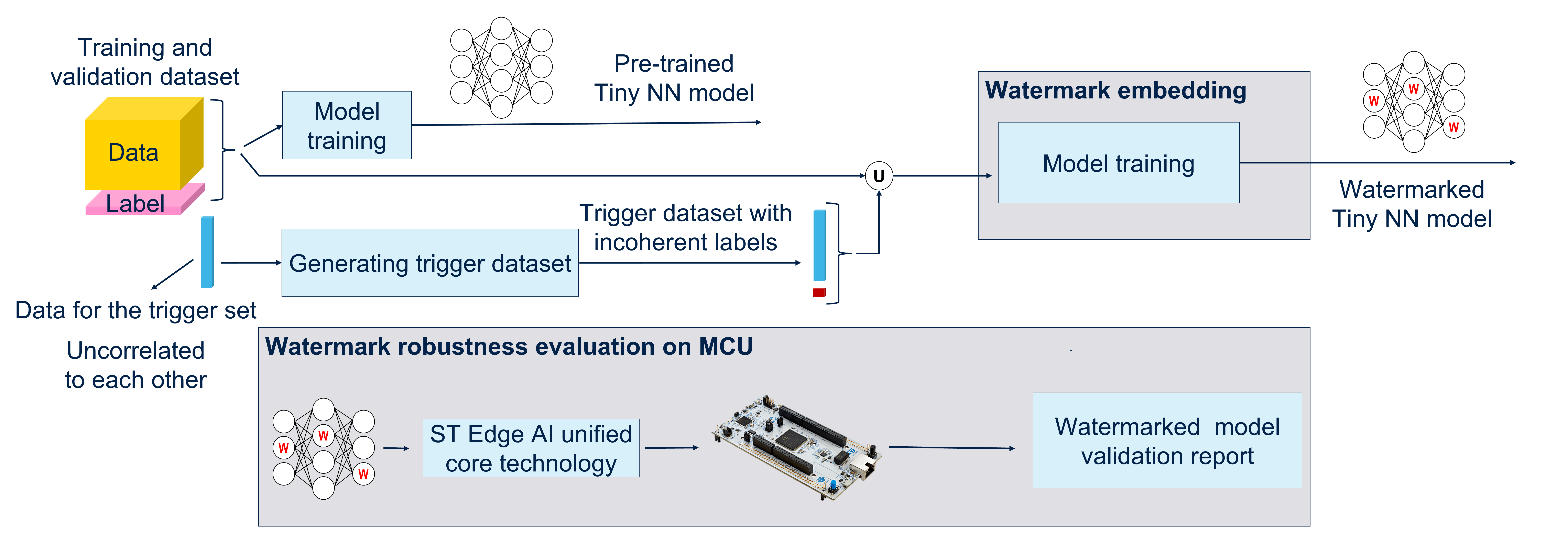
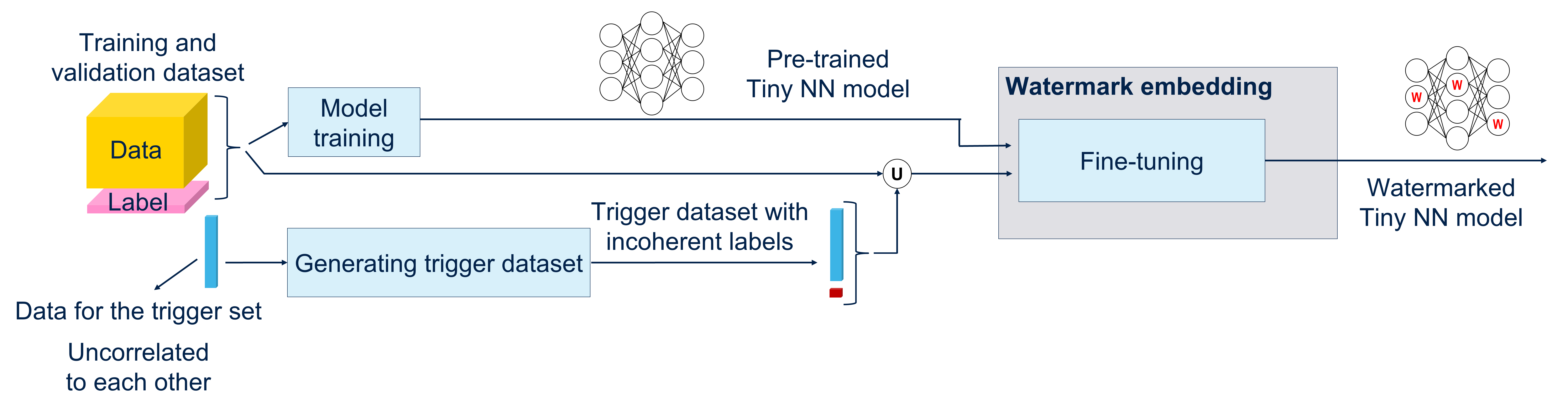
Fixed some problem for Watermark Embed in the notebook.
Added requirements. Minor changes in README.txt. Exemplary trigger pics added.
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:


95.9 KB
63.9 KB
76.5 KB
27.3 KB
21.4 KB
96.9 KB
25.8 KB
134 KB
48.9 KB
71.2 KB
29.2 KB
150 KB
114 KB
49.8 KB
104 KB